Xcode change target name[]
below step works for Xcode 4.6.2
- in Xcode click project icon, in TARGETS direct edit target name, such as: change change ipadcn to cn_ipad
- in Build Settings -- Package, change the Product Name, such as: change ipadcn to cn_ipad
- Xcode close project, delete the xcode auto generate files, such as: *.xcscheme, ..., Xcode Re-open the project
- If you meet Simulate error "failed to attach to process id 0", you need clean Simulator content.
- reset simulator: in menu iOS Simulator --> Reset Content and Settings...
- back to xcode, in menu Window --> Organizer --> Projects --> Delete Derived Data
find iOS simulator location[]
- Go to ~/Applications, and right-click Xcode.
- Select “Show Package Contents”. A folder opens.
- Browse through the folder structure to “Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneSimulator.platform/Developer/Applications/”
- There you’ll see the “iOS Simulator.app” — it’s best to add it to the dock, so that you do not need to go through these steps again.
- Close all the folders, as you won’t need them to use the iOS Simulator.
- Start iOS Simulator from the Dock.
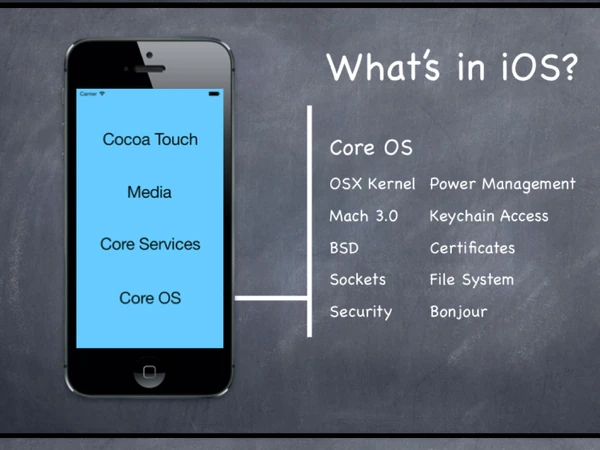
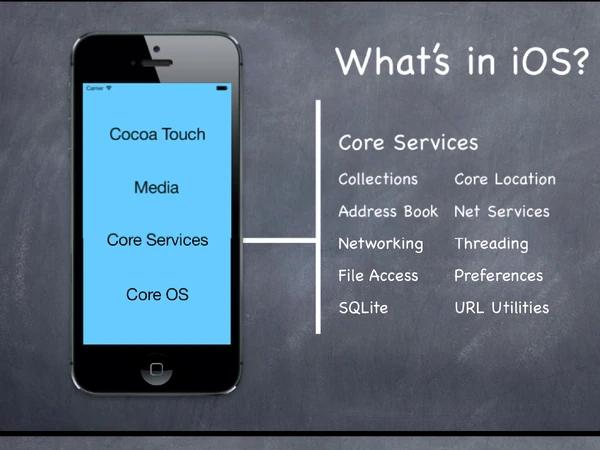
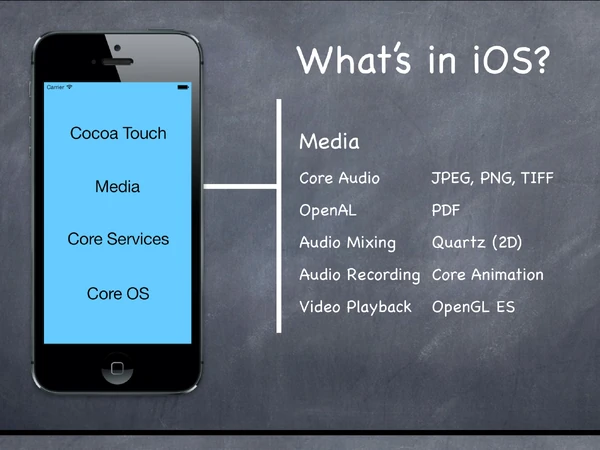
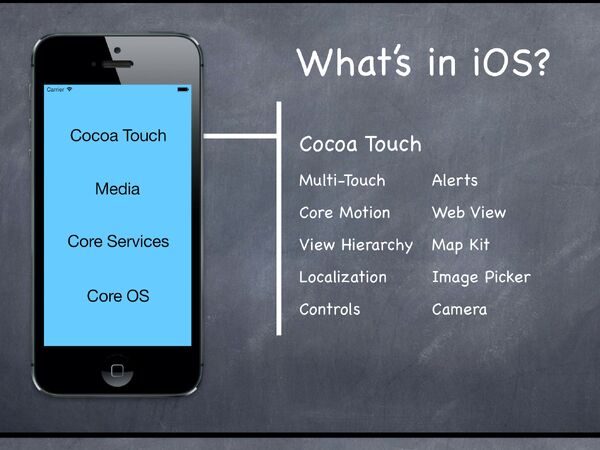
What's in ios[]
Core OS[]
Core Services[]
Meida[]
Cocoa Touch[]
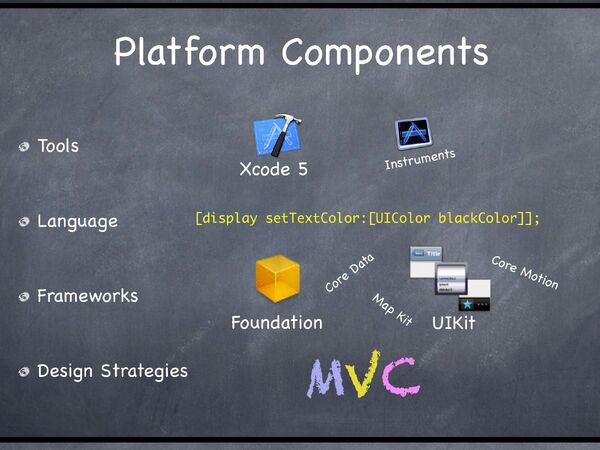
Platform Components[]
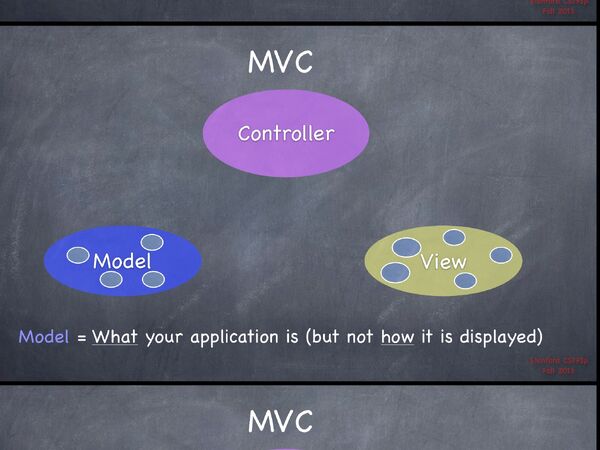
MVC[]
Divide objects in your program into 3 "camps".
- Model = What your application is (but not how it displayed)
- Controller = How your model is presented to the user (UI Logic)
- View = Your Controllers minions
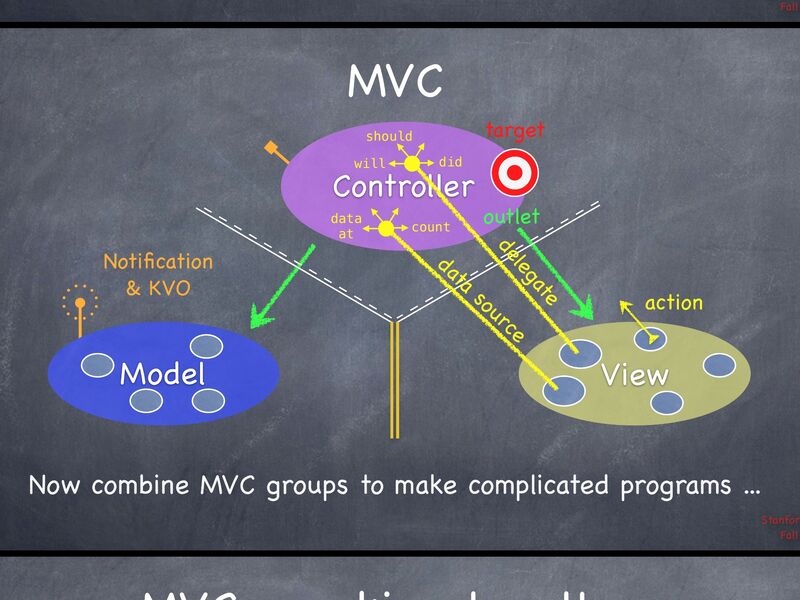
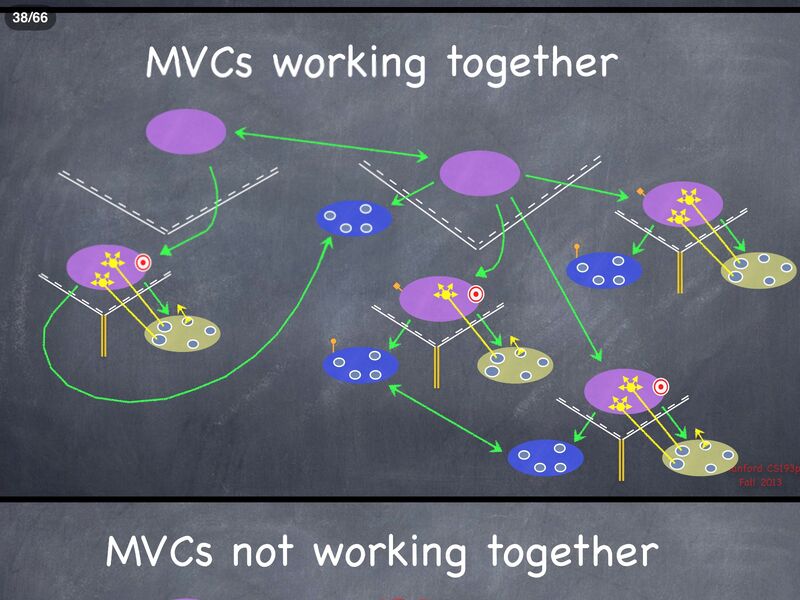
MVC Communication[]
- Controllers can always talk directly to their Model.
- Controllers can also talk directly to their View.
- The Model and View should never speak to each other.
- Can the View speak to it's Controller?
- The Controller can drop a target on itself.
- Then hand out an action to the View.
- The View sends the action when things happen in the UI.
- Sometimes the View needs to synchronize with the Controller.
- The Controller set itself as the View's delegate.
- The delegate is set via a protocol (i.e. it's "blind" to class)
- Views do not own the data they display.
- So, if needed, they have a protocol to acquire it.
- Controllers are almost always the data source (not Model).
- Controllers interpret/format Model information for the View.
- Can the Model talk directly to the Controller?
- No. The Model is (should be) UI independent.
- So what if the Model has information to update or something?
- It use a "radio station" - like broadcast mechanism.
- Controllers (or other Model) "turn in" to interesting staff.
- A View might "turn in" , but probably not to a Model's "station".